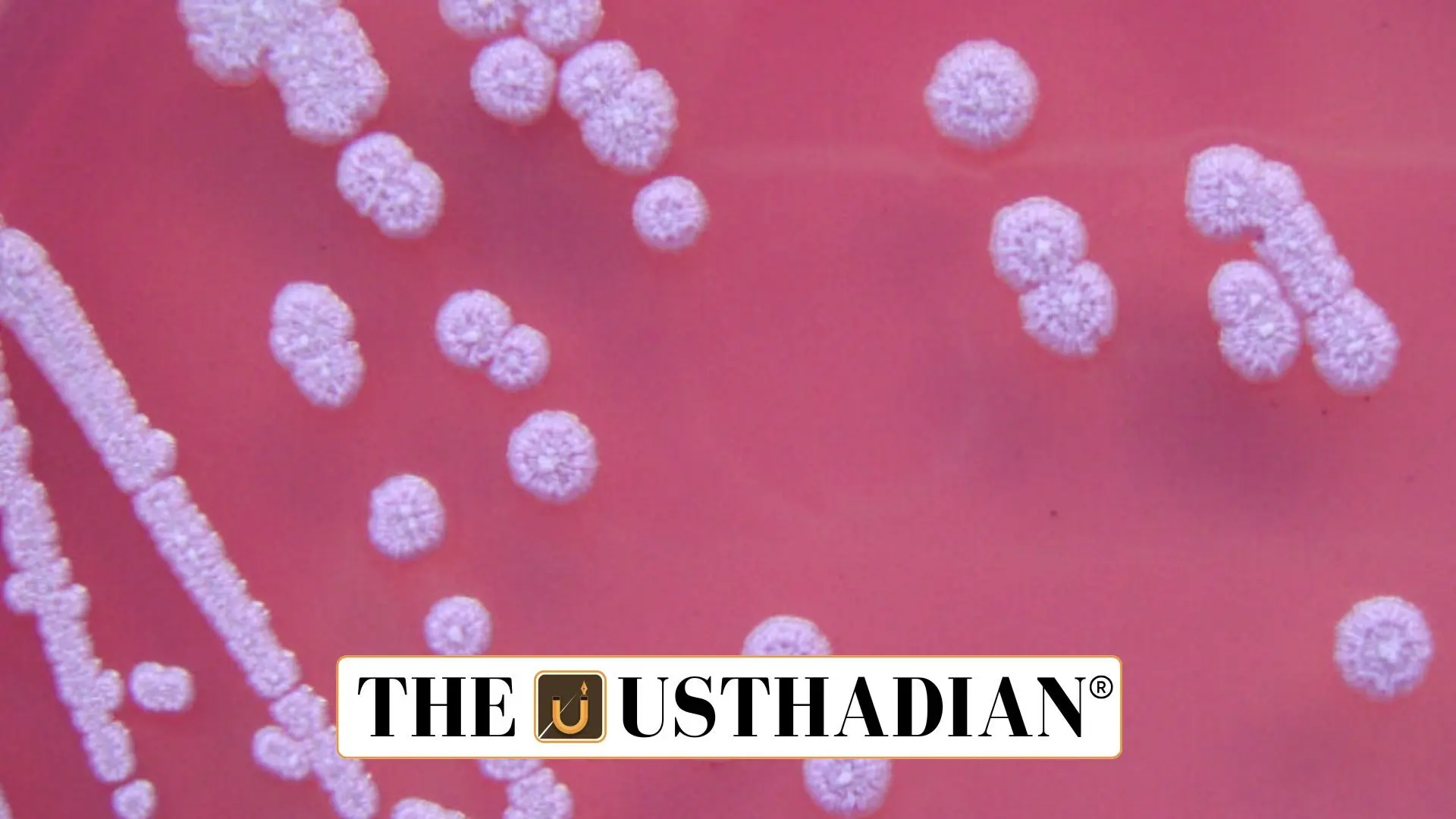
What Is Melioidosis and Why It Matters
Melioidosis in Odisha: Climate-Linked Disease Emerges as Public Health Concern: Melioidosis is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Burkholderia pseudomallei, commonly found in contaminated soil and water. People usually acquire the infection through skin abrasions, inhalation, or ingestion during exposure to these environmental sources. The disease presents in multiple forms, ranging from localized abscesses and skin infections to fatal cases of pneumonia and septicemia, with mortality rates reaching up to 50% in severe conditions. What makes melioidosis particularly challenging is its nonspecific symptoms and similarity to other diseases, often leading to late diagnosis and higher fatality.
Climate Conditions Fueling Its Spread
Recent studies highlight that melioidosis cases spike during monsoon and post-monsoon periods, confirming the influence of environmental factors such as rainfall and temperature on the bacteria’s survival and transmission. The warm, wet conditions common to tropical regions like Odisha make it an ideal breeding ground for Burkholderia pseudomallei, especially when combined with frequent flooding and poor drainage, which increase contact with infected soil and water.
Odisha’s Research Model: Science Meets Climate Analytics
A joint study by AIIMS Bhubaneswar and IIT Bhubaneswar marks a significant step forward in understanding melioidosis transmission. The team analysed nine years of meteorological and infection data, mapping it across Odisha to identify high-risk zones. This interdisciplinary approach between microbiologists and climate scientists is a model of how data-driven disease surveillance can help detect patterns and anticipate future outbreaks.
High-Risk Districts and Public Exposure
The research revealed that districts like Cuttack, Khordha, Jajpur, and Balasore are most vulnerable to melioidosis. These areas not only experience high monsoon rainfall but also have dense populations, increasing the likelihood of human exposure. The findings serve as a wake-up call for local health departments to integrate geographic risk mapping into public health plans and awareness campaigns in these regions.
Climate Change: A Threat Multiplier for Infections
Climate change is amplifying the threat of diseases like melioidosis by shifting rainfall patterns, causing more frequent floods, and extending transmission seasons. With extreme weather events becoming more common, regions previously unaffected may soon face new microbial threats. This makes it essential for India’s public health infrastructure to incorporate climate models and forecasting tools into its disease monitoring systems.
STATIC GK SNAPSHOT
Melioidosis in Odisha: Climate-Linked Disease Emerges as Public Health Concern:
| Aspect | Details |
| Disease Name | Melioidosis |
| Causing Agent | Burkholderia pseudomallei |
| Transmission | Contact with contaminated soil/water (skin cuts, inhalation) |
| Fatality Rate | Up to 50% in severe untreated cases |
| High-Risk States in India | Odisha (Cuttack, Khordha, Jajpur, Balasore) |
| Key Research Bodies | AIIMS Bhubaneswar, IIT Bhubaneswar |
| Climate Link | High rainfall, monsoon floods, warm temperatures |
| Global Relevance | South Asia contributes a large share of global melioidosis cases |
| Future Strategy | Climate-integrated disease mapping and surveillance |