Discovery from Banaras Hindu University Sparks Agricultural Alert
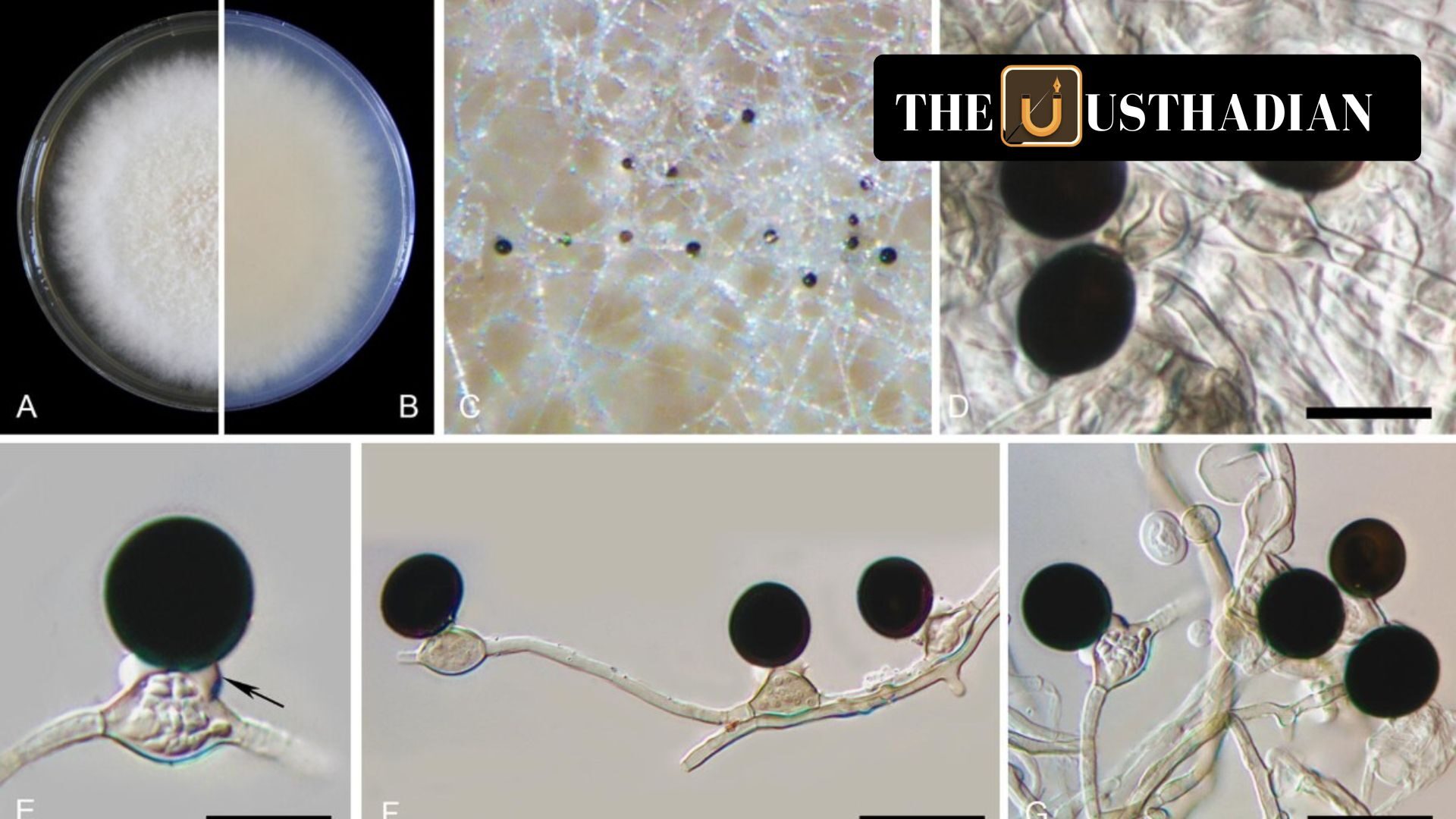
Epicoccum indicum: A New Fungal Threat to Medicinal Plant Vetiver Identified : On January 28, 2025, a team of researchers from Banaras Hindu University (BHU) announced the discovery of a new phytopathogenic fungus species, named Epicoccum indicum. This fungus has been identified as the causal agent of a rising leaf spot disease affecting Chrysopogon zizanioides—better known to the public as vetiver or khus. The development has raised concerns about the health of this economically and medicinally valuable plant.
How Was Epicoccum indicum Identified?
The identification process was scientifically rigorous. Researchers combined morpho-cultural observations—like colony color and spore shape—with multigene molecular phylogenetic analysis, which involves comparing DNA sequences from multiple genes. This advanced method revealed that Epicoccum indicum forms a distinct genetic clade, confirming that it is indeed a newly discovered species and not a variant of a known one.
Why Vetiver Matters
Vetiver is more than just a grass. Chrysopogon zizanioides has a long-standing reputation in Ayurvedic and traditional medicine. It is commonly used to treat pain, fevers, skin infections, and inflammation. Beyond its medicinal value, its roots are used for making perfumes, mats, and natural coolers, especially in summer.
Interestingly, the word “vetiver” comes from Tamil, meaning “root that is dug up”—an appropriate name, as the plant’s usefulness lies mostly in its aromatic roots. In northern India, it’s referred to as “khus”, which should not be mistaken for “khus khus”, a completely different plant (poppy seeds).
Understanding Leaf Spot Disease
The major concern now is the spread of leaf spot disease, which this fungus causes. Typically, leaf spot appears as brown or yellow patches on leaves, sometimes with a dark, necrotic center. These diseases are not just cosmetic; they limit photosynthesis and can lead to massive leaf loss, ultimately weakening or killing the plant.
Such diseases are more likely to spread in humid and wet climates, especially during monsoons or in fields with poor drainage. The spores are easily carried by wind, rain splashes, or even irrigation water.
The Bigger Picture: Fungal Diseases and Their Impact
Leaf spot is just one among many plant diseases. Others include leaf rust, blights, and downy mildew, each affecting different species and requiring specific treatments. The discovery of Epicoccum indicum adds to a growing list of new pathogens threatening India’s agricultural and medicinal biodiversity.
Static GK Snapshot
Epicoccum indicum: A New Fungal Threat to Medicinal Plant Vetiver Identified :
| Topic | Fact Highlight |
| Fungal Species Name | Epicoccum indicum |
| Discovered by | Researchers at Banaras Hindu University |
| Affected Plant | Vetiver / Chrysopogon zizanioides |
| Disease Type | Leaf Spot Disease |
| Etymology of ‘Vetiver’ | From Tamil, meaning “root that is dug up” |
| Identification Method | Multigene molecular phylogenetic analysis |